In this section you will find all the answers to the most frequently asked questions related to: linear technology, solutions through linear motors, industrial automation and robotics.
Which linear guide is most suitable for my application?
What types of linear motor exist?
There are four different types: ironcore, ironless, tubular and piezoelectric. To learn more about each type you can access our blog article “Linear Motors: what are they and which types are there ?”.
How does a linear motor work?
A linear motor’s functioning underlies the same physical principle that in the case of ‘traditional’ linear motors, that is, a force is generated thanks to the passing of electrical power through a magnetic field. This magnetic field is generated via permanent magnets of Neodimium. To learn more about each type you can access our blog article “Linear Motors: what are they and which types are there ?”.
How to protect linear motors?
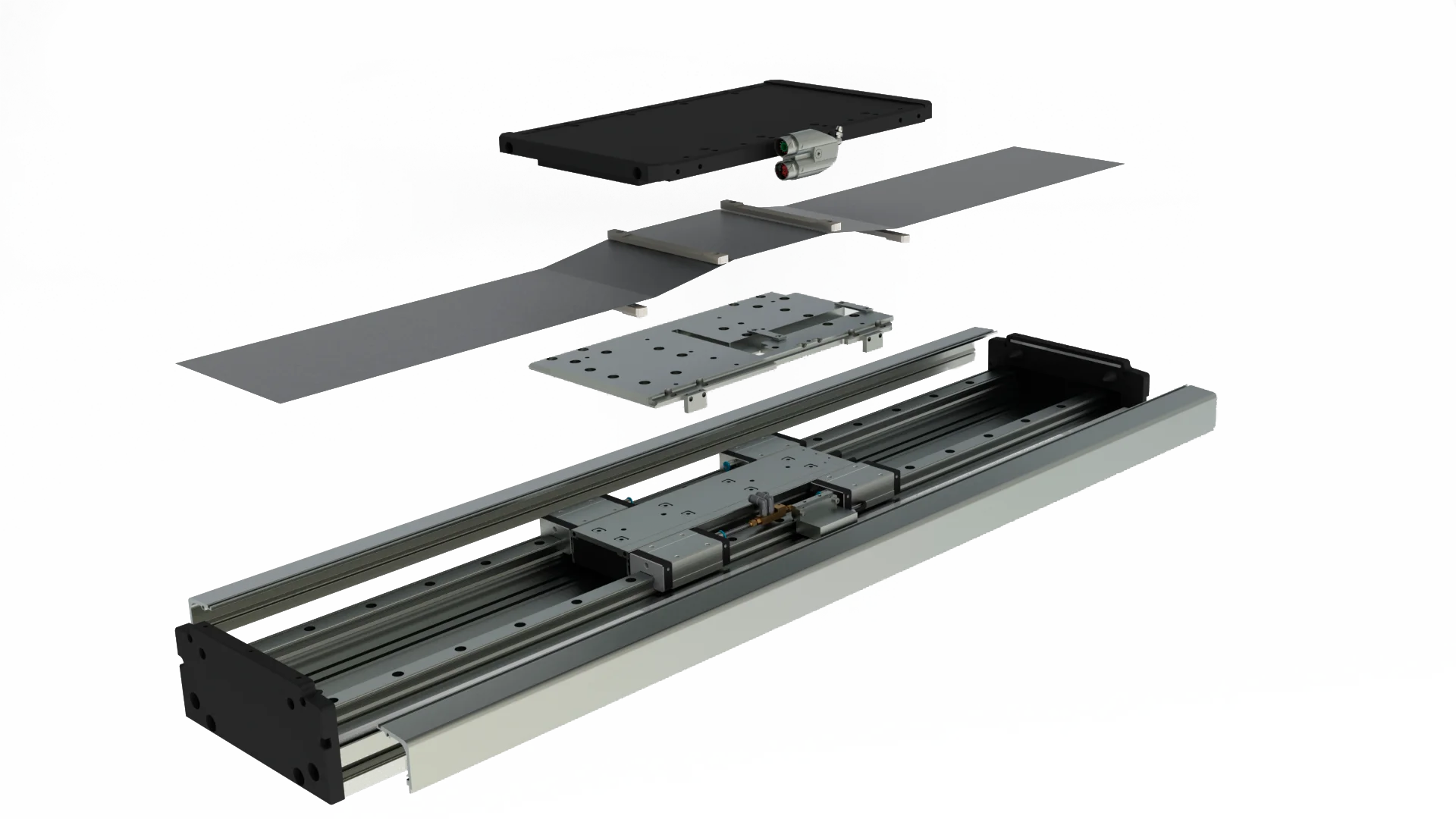
To protect a stage with a linear motor, there are flexible and rigid covers. The choose of one or the other will depend on the needs of the machine regarding the work environment where it is used. It is advised to use an inductive encoder, as it is a robust component that resists dirt and other elements well. For more information you can access our video “How to protect linear motors?”.
How to prevent a vertical linear motor from falling?
There are three possible solutions: pneumatic or electromechanical brakes, compensation by magnetic load and compensation by pneumatic cylinder. For more information you can access the explanatory video “What happens with a linear motor in vertical position?”.
In linear motion, how is linear power calculated?
The linear power calculation formula is: P (kW) = M x V /100000 x µ, kW. For more information you can access our article “Linear movement: Power calculation”.






Get Social